
This is the third and final part of my pilgrimage account from St. Cuthbert’s Way and beyond.
The previous installments can be found at these links:
Grace and Beauty on Holy Island
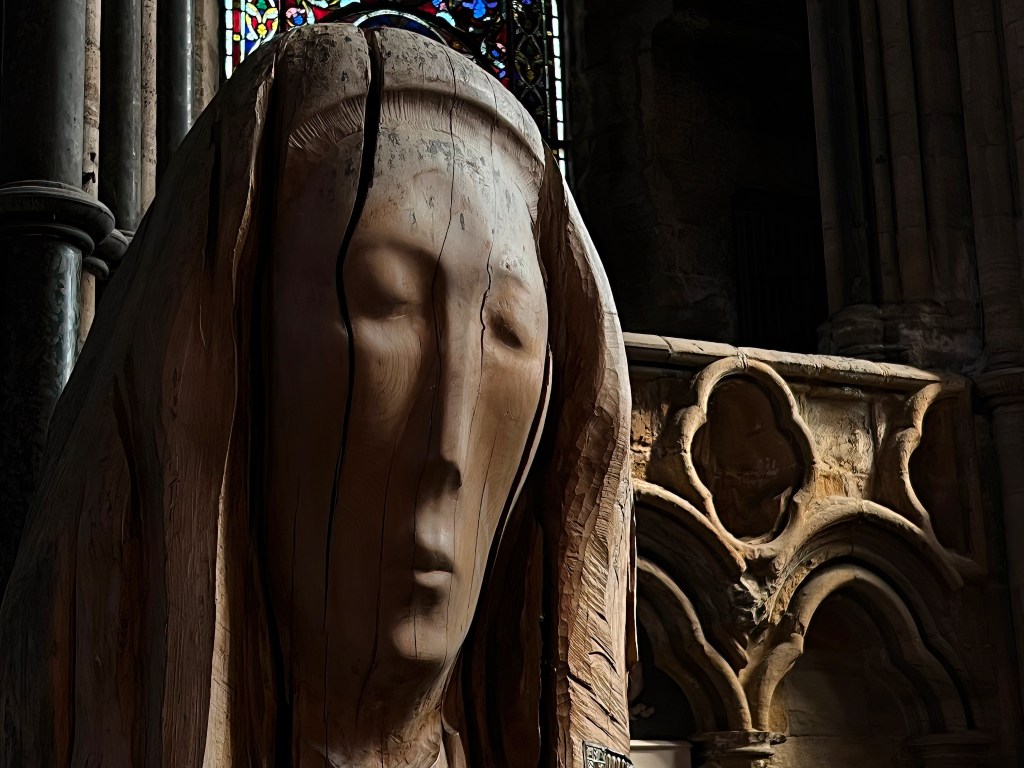
The original wooden sculpture of the Lindisfarne monks carrying Cuthbert’s coffin to safety is in St. Mary the Virgin on Holy Island. This bronze version is in Durham’s Millennium Square, below the cathedral where Cuthbert’s long journey ended at last. It seems a bit lost in the bleak vacancy of the square’s secular space (an effort to move the 2.5 ton sculpture to the cathedral grounds failed), but that makes it a parable of the Church in an age of religious displacement, wandering in search of an abiding home. The change-ringing bells were sounding from a nearby church when I shot this video.
“By faith … he set out without knowing where he was going …
He looked forward to a city with firm foundations,
whose architect and builder is God.” (Hebrews 11:9-10)
After the peripatetic St. Cuthbert died in his island hermitage, his body continued to wander for nearly nine centuries: to the mainland for burial in the monastery church (687) … into a newly built sepulcher (698) … inland to various temporary hiding places during 8 years of Viking terror (875-883) … under the protection of a new regional king, to Cuncasestre (Chester-le-Street), where a new church held his shrine for 112 years (883-995) … fleeing new Norse threats, south to Ripon for 4 months (995) … north to Wrdelau, near the River Wear, where the coffin-bearing cart broke down, as if the saint himself were refusing to go any further (995, for 3 days of prayer for guidance) … spurred by a vision (or was it the assistance of a dairymaid searching for her cow?), the saint’s entourage moved his remains to the nearby Dunholme (“Hill Island”), a naturally protected peninsula rising above a loop in the river, where they built a rough shelter (995-999) … then into a succession of more permanent structures on Dunholme (999-1069) … after 70 years, under threat from William the Conqueror, the Norman king who was “harrying the north,” a brief return to his old monastery at Lindisfarne (1069-1070) … back to the church on Dunholme, where Durham was becoming a major English settlement (1070-1104) … translated into a shrine behind the high altar in the completed east end of the great Norman cathedral-in-progress (1104) … moved into a more richly embellished shrine set upon a raised floor (1280) … after the stripping and destruction of the shrine under Henry VIII, reburied in an unadorned vault in the same location (1542), where it remains to this day.

— Hugh of St. Victor, The Mystical Mirror of the Church
How awesome is this place!
Truly, this is none other than the house of God;
it is the gate of heaven.— Genesis 28:17
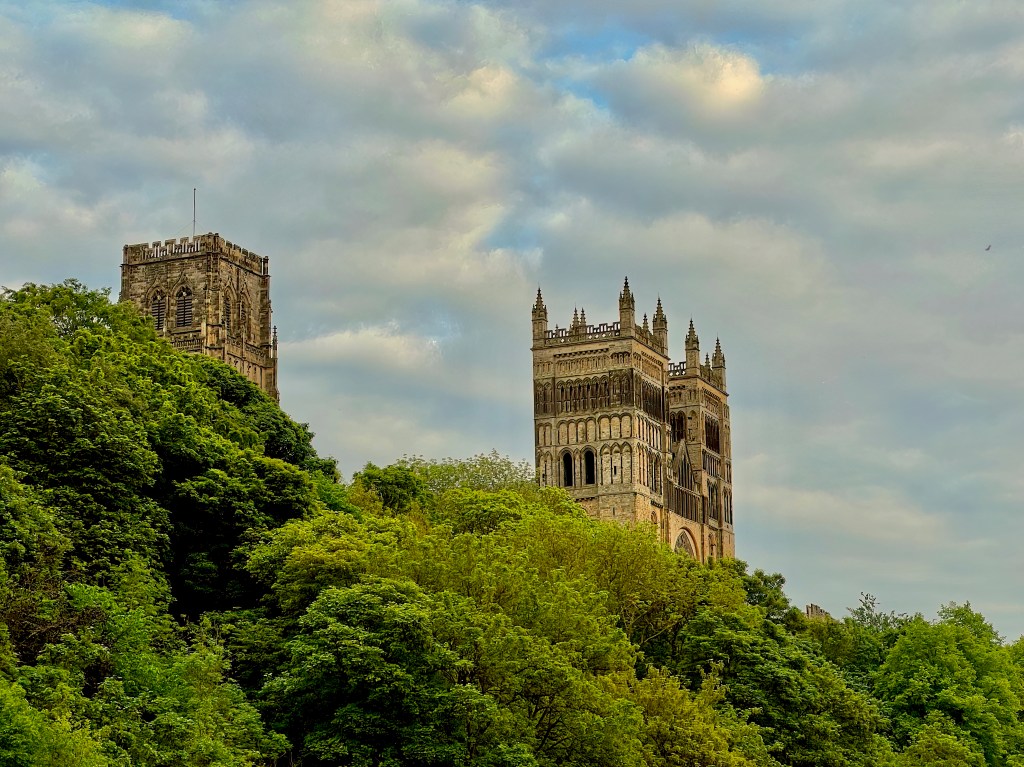
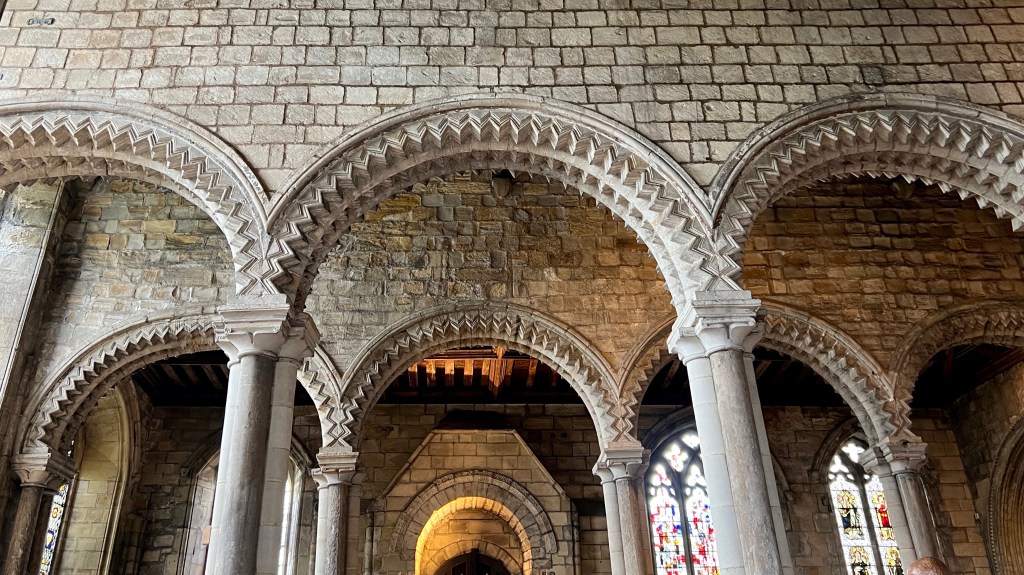
The cathedral raised to shelter Cuthbert’s shrine is one of the world’s most magnificent buildings. Set high on the rock of Dunholme, its dominant presence is softened by the lush foliage veiling its base. A Romantic might imagine it a miracle of stone, springing up supernaturally from the forest primeval. In fact, its monumental architecture was part of a dramatic upwelling of energy, intellect and confidence surging throughout Europe at the dawn of the twelfth century. Cities and universities, trade and travel, churches and cathedrals all burst into bloom in that sudden quickening of western civilization.
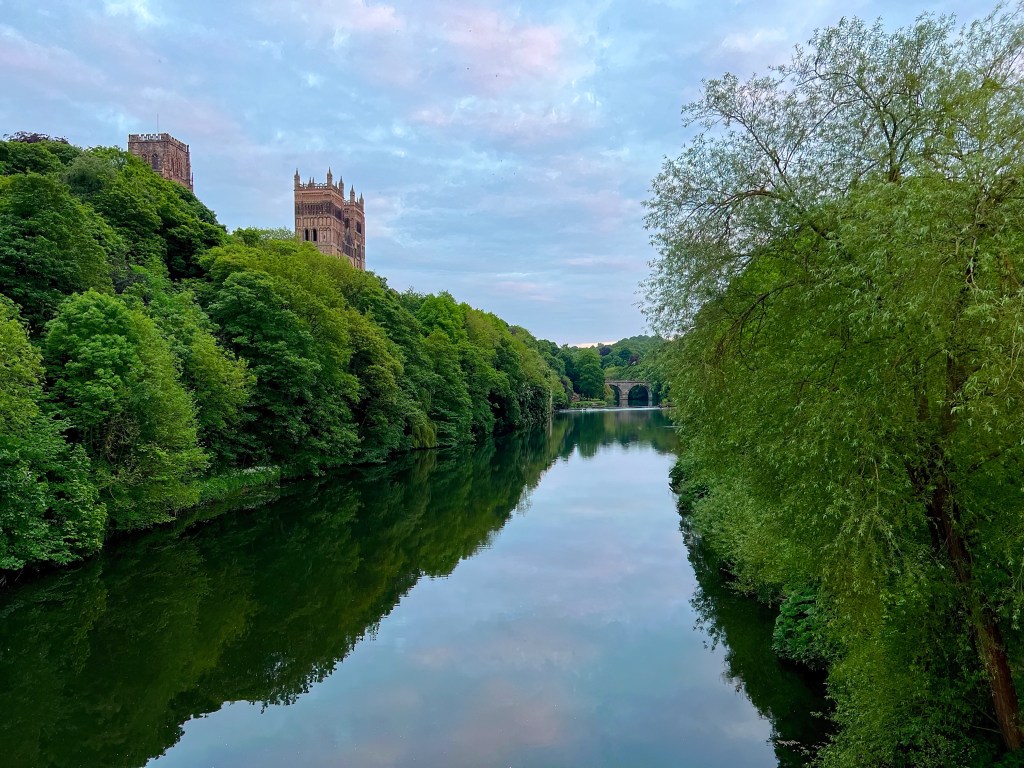
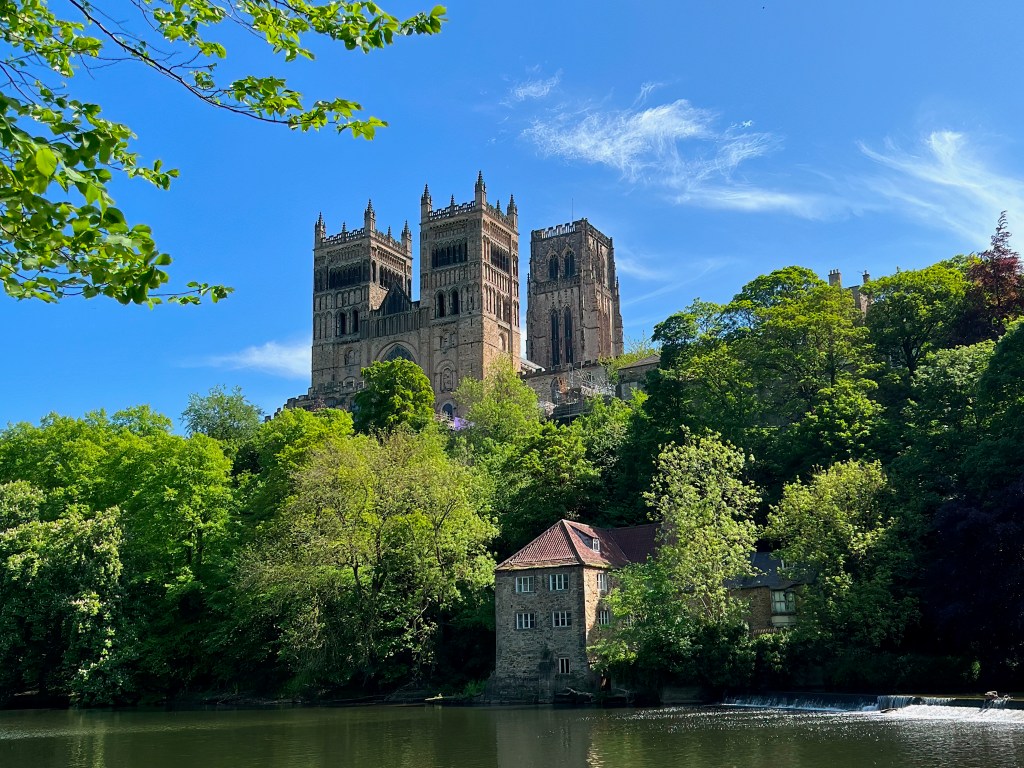
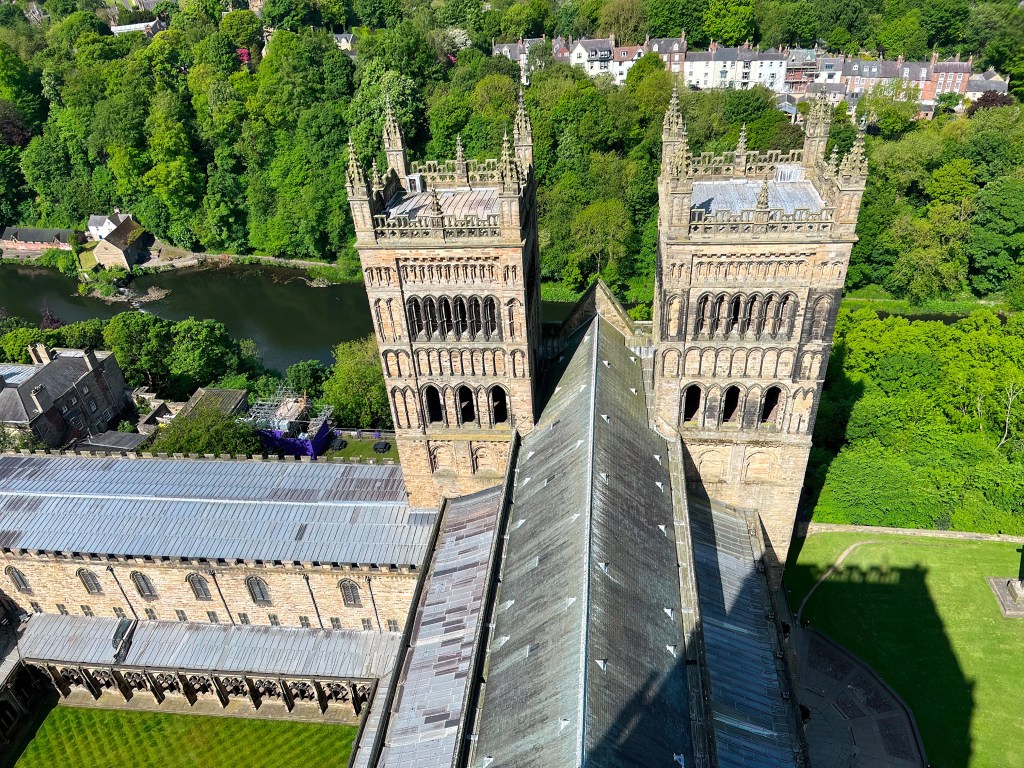



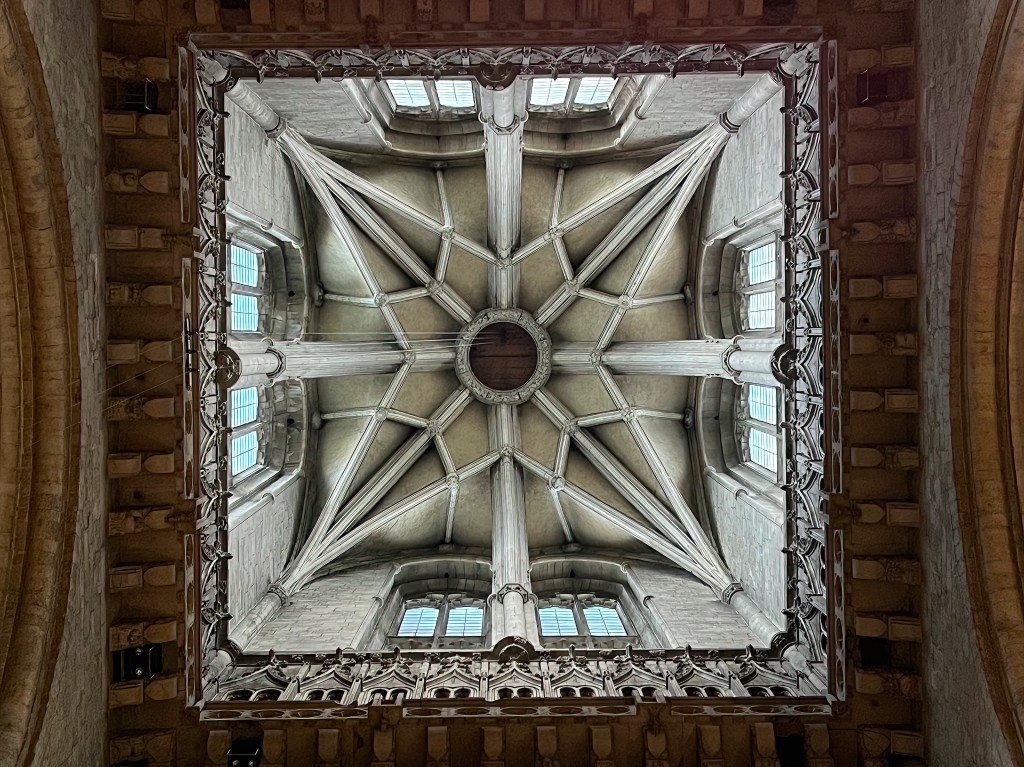
In England, the first cathedrals were begun in the Romanesque style imported from Normandy. Durham Cathedral is the only one to retain the purity of its original Norman craftsmanship and design, although the western towers reflect the emerging Gothic style, and the fifteenth-century crossing tower, replacing a previous tower damaged by lightning, is late Gothic.
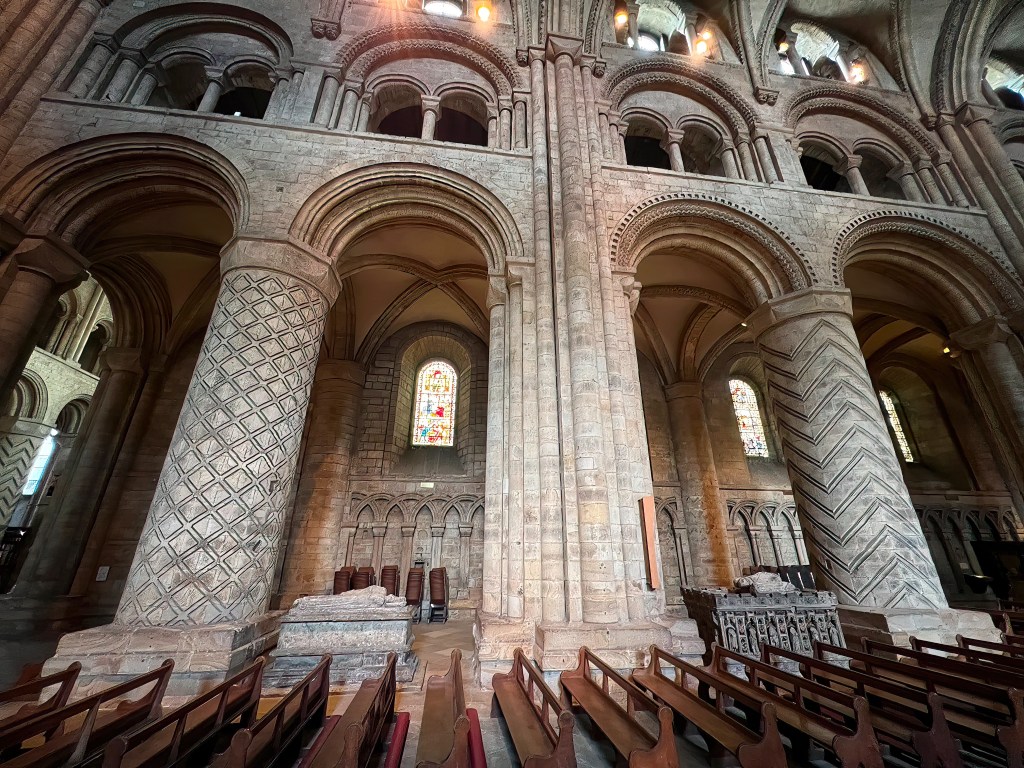


Some large churches employ a repetition of identical columns, topped by horizontal bands of wall, windows or arches, sweeping us forward toward the altar. But Durham Cathedral created an alternating system of columns and piers, dividing the horizontal space into bays. This structural rhythm affects the way our bodies move through the space. As theologian J. G. Davies explains,
“The consequence is that equal strophes, following each other down the vista of the nave, have given way to alternating strong and weak stresses, i.e., of piers alternating with columns … The nave walls are now a linear sequence of individualized parts that retard any rapid flow towards the sanctuary.” [i]
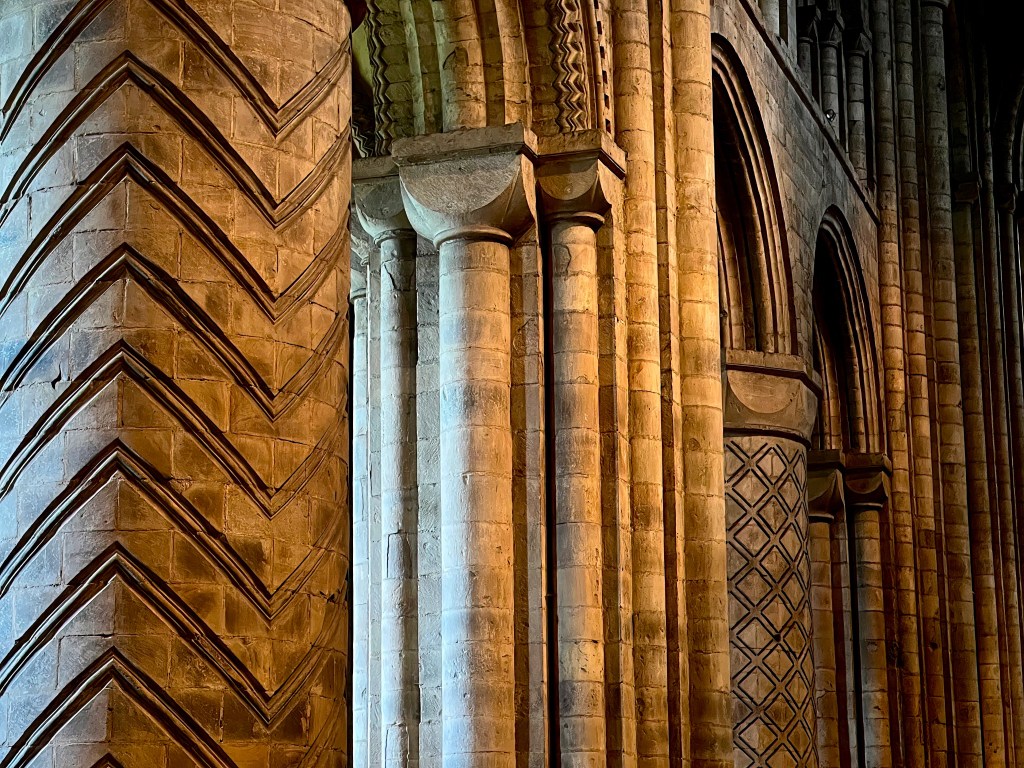


While later cathedrals would pursue the Gothic dematerialization of the built structure, with walls becoming thinner and transparent with glass, and ceilings reaching toward the sky, Durham exudes a sense of solidity and weight. Thick walls and massive pillars, supporting the heavy stone roof, signify permanence and strength. Although such features can feel oppressive in more primitive Romanesque churches, nothing here feels inert or stifling. The articulation of details, such as rib vaults, geometric patterns, variations in column design, blank arcades, and a recessed series of arch moldings, all serve to enliven and animate the whole without compromising the overall simplicity, austerity and calm befitting its origins as a monastic enclosure.
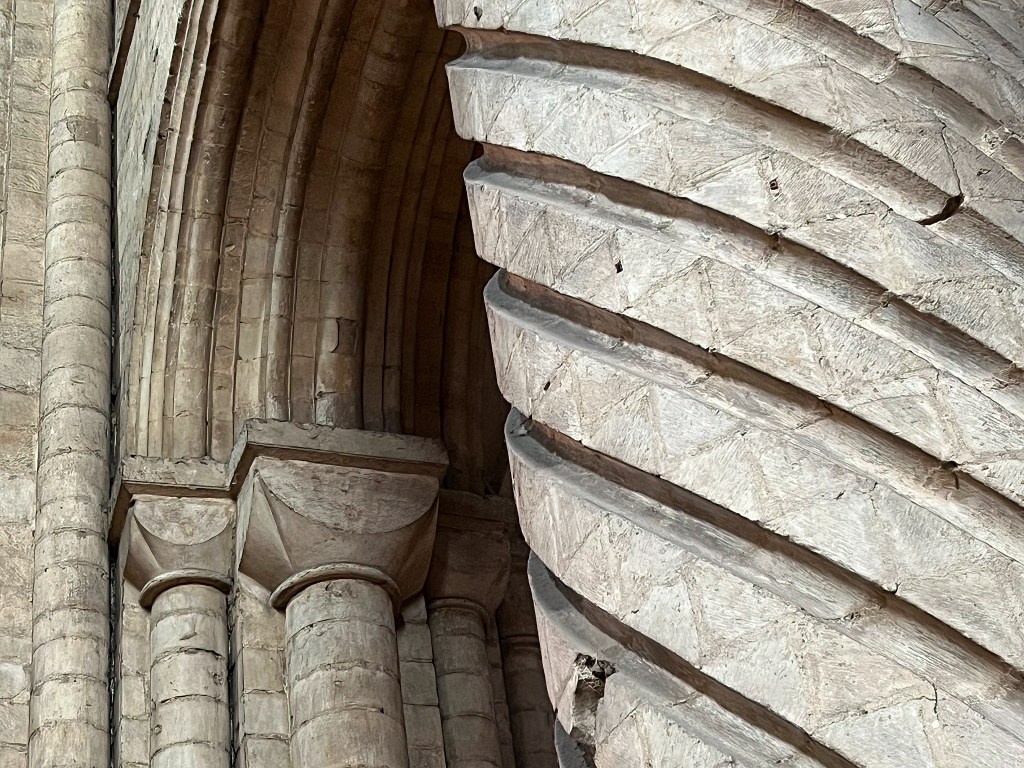

“The architect can work with the empty space—the cavity—between the solids, and consider the forming of that space as the real meaning of architecture.”
— Steen Eiler Rasmussen [ii]
The cathedral is not simply a collection of solid parts. It is also the empty space shaped by its physical components. Length (horizontality) and height (verticality) are the fundamental dimensions of this space. The path between entrance and altar (or shrine) signifies life as a pilgrimage: there is a distance to be traversed, but the goal may yet be reached. At the same time, an interior that soars above our heads keeps us mindful of the Transcendent: it cannot be grasped or possessed, but it awakens our aspiration for a greater, higher reality. And throughout the whole, the interplay of light and shadow, immensity and intimacy, flow and obstacle, openness and containment, hiding and revealing lures us deeper into the Mystery beyond words.
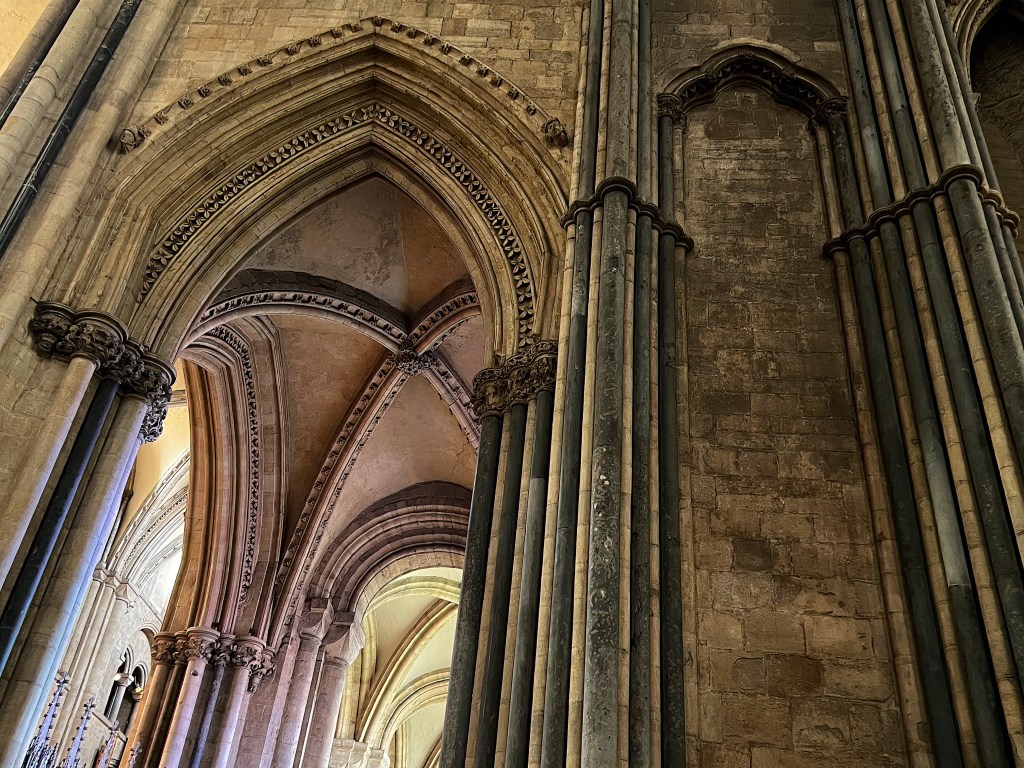

“[When] work reaches a maximum of intensity, when it has been made with the best quality of execution, when it has reached perfection … When this happens, the places start to radiate. They radiate in a physical way and determine what I call ‘ineffable space,’ that is to say, a space that does not depend on dimensions but on the quality of its perfection. It belongs to the dimension of the ineffable, of that which cannot be said.” — Le Corbusier [iii]
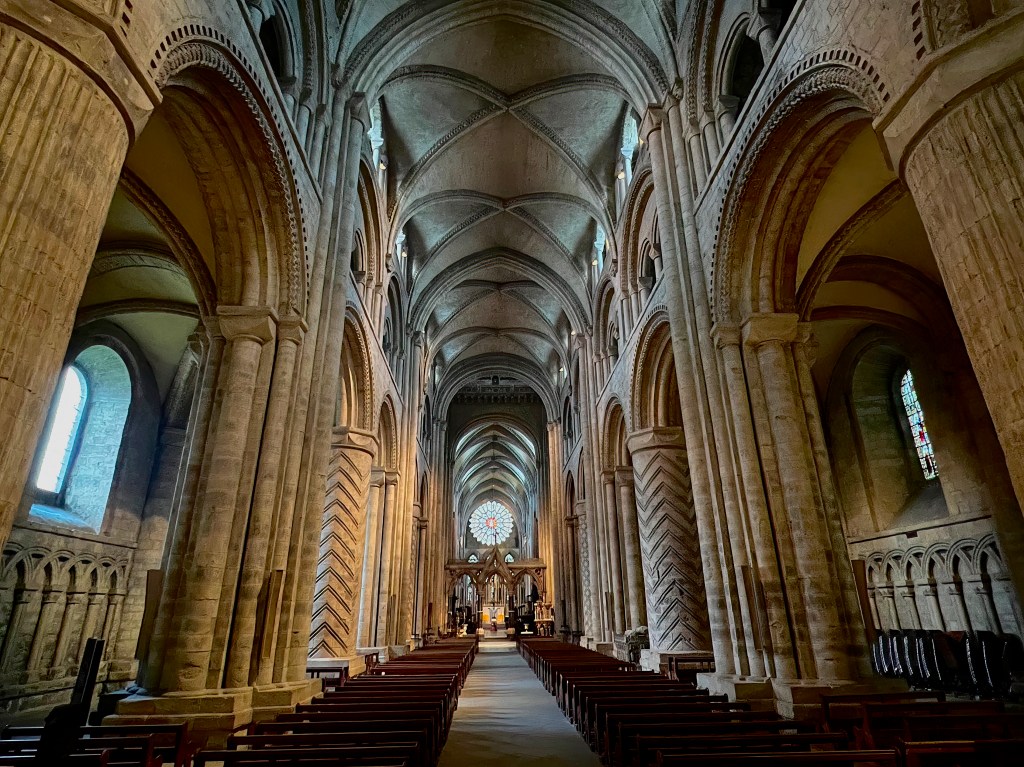

Some have argued that a church is not a place for a casual visitor to have a worship experience. It is not a shelter for an altar or holy object, but for an assembly, and it has no meaning or symbolic power apart from its liturgical function. At the other end of the spectrum is Joseph Campbell’s assertion that one can be “reborn spiritually by entering and leaving a church.”
For me, Durham Cathedral is both/and, not either/or. Many of its 700,000 annual visitors may not share the symbols, narratives, and rituals which have shaped its construction and history, but only the deadest of souls would remain unaffected by this sacred space. We all need “places which allure us with their beauty, which call us to a halt, which refresh us with their charm and are a positive ease and delight for the spirit.” [iv] We all need rooms that care.
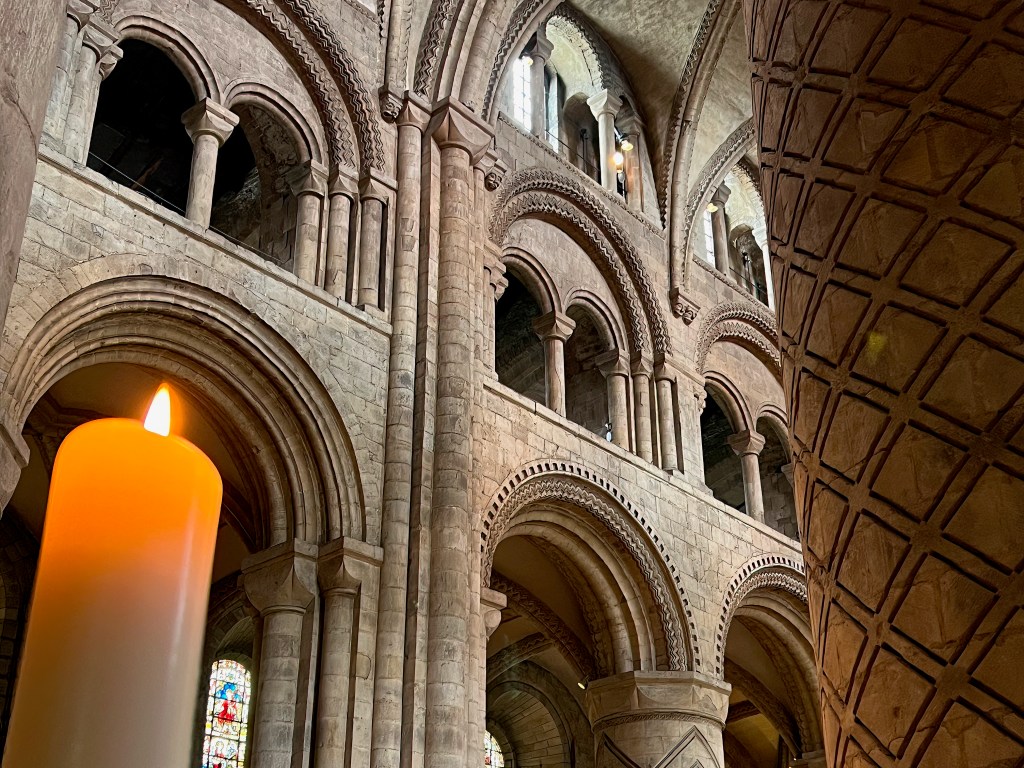

G. K. Chesterton said that the Church is “the only thing which saves a man from the degrading slavery of being a child of his age.” [v] Cathedrals are no longer centers around which whole cities or cultures are organized, nor do they hold an exclusive copyright on the sacred, but they remain indispensable preserves of experiences and perspectives necessary for the health of our souls and the life of the world. When our medieval predecessors entered their cathedrals, “they were the enraptured witnesses of a new way of seeing.” [vi] And, I would add, participants in a new way of being. May it be ever so.
The physical act of wandering through Durham Cathedral exerts a formative effect on body, heart, and intellect, deepening the sense of life as pilgrimage and passage. As our eyes and our feet move through the cathedral along its system of paths and enclosures, we feel the pull toward a goal, be it altar or shrine. At the same time, the way is strewn with burning bushes, inviting us to turn aside for a moment—or pause to look up—that we may receive and ponder their wordless message of holy presence.
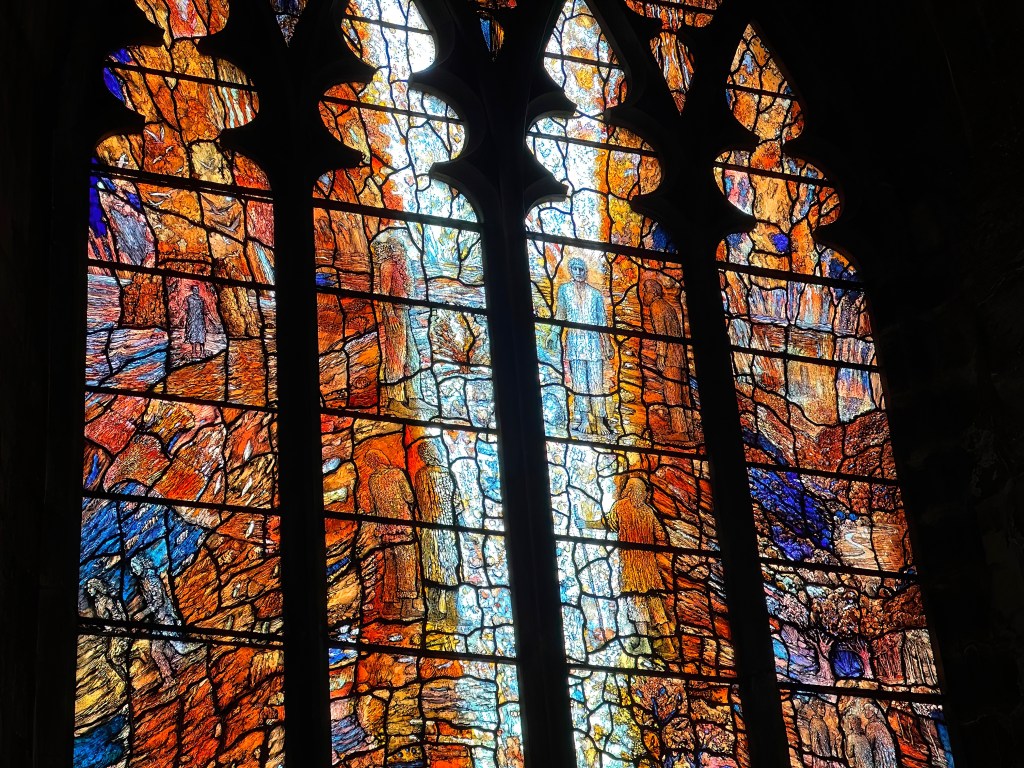
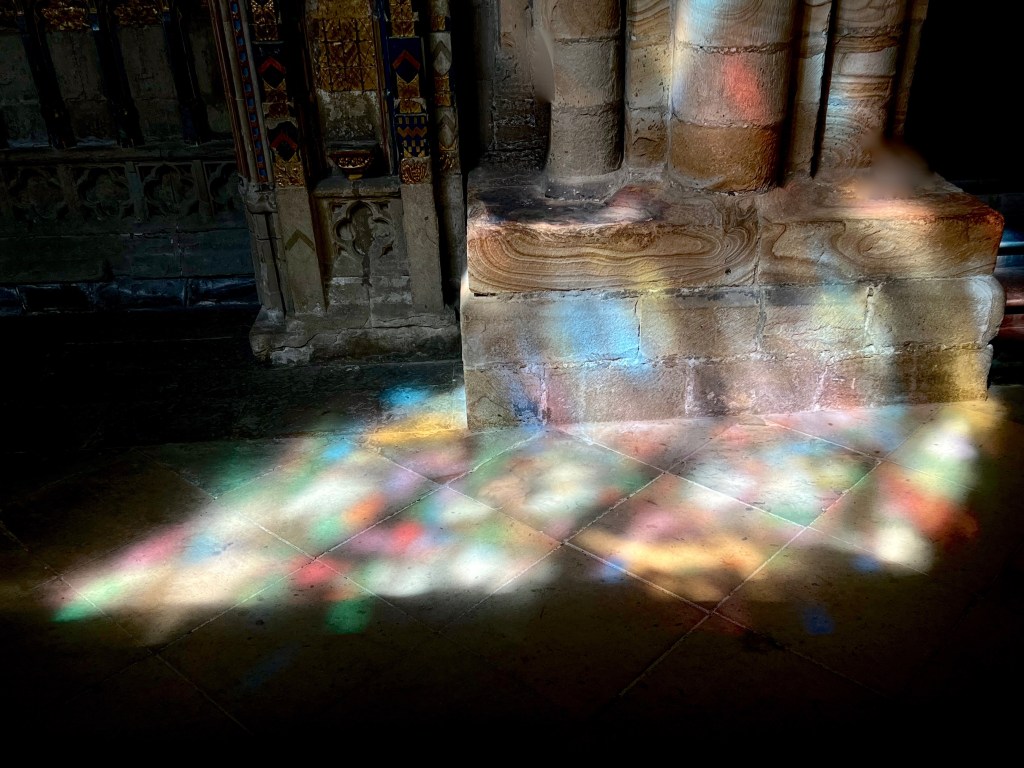




At the east end of the cathedral, behind the high altar, is the tomb of St. Cuthbert. Stripped of its once lavish adornments by the decline of medieval pilgrimage and the predatory greed of Henry VIII, its quiet simplicity seems much more suited to the spirit of the humble saint who preferred bare and wild places.
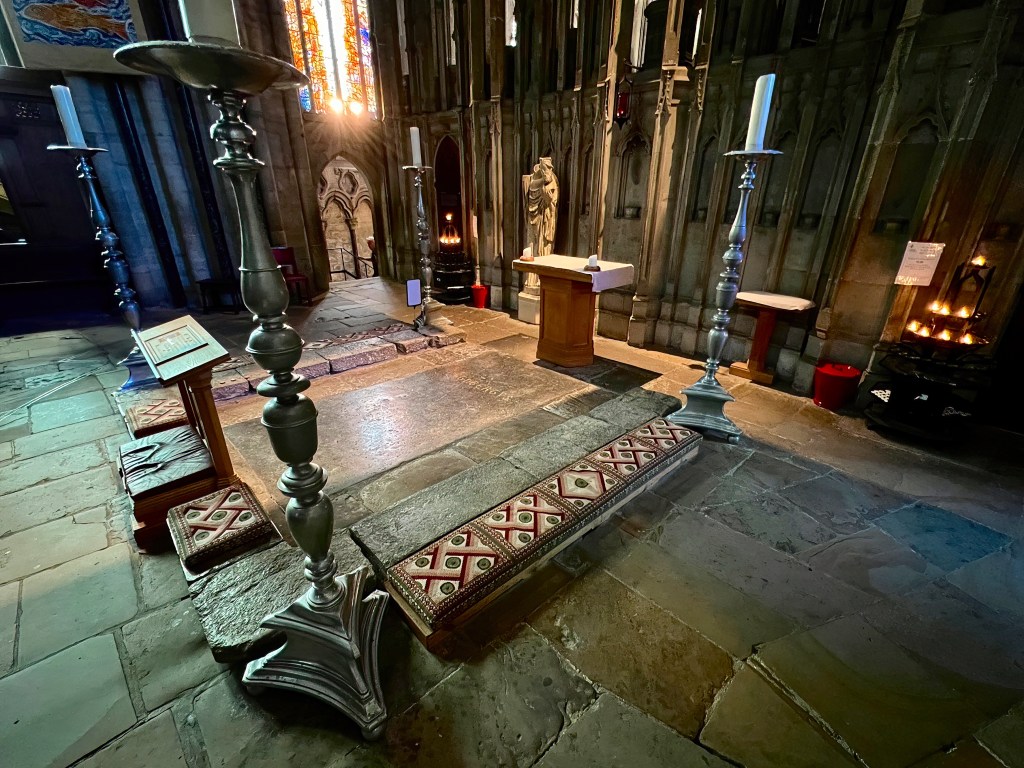

When I reached the feretory, I ascended the steps to the tomb. Here was my journey’s end. As T. S. Eliot said of another holy place,
You are not here to verify,
Instruct yourself, or inform curiosity
Or carry report. You are here to kneel
Where prayer has been valid. [vii]
And so I did. I gave thanks to God and his saint for the beautiful pilgrimage, remembering the beauty of the people and the wonders all along the way from Melrose to Holy Island to Durham. I reflected on the stories of Cuthbert and his times, his warm spirit and faithful heart, feeling gratitude for the gift of saints who show us how. But I did not linger. What the angel said on Easter morning applies to every tomb: He is not here. Cuthbert still walks the paths of memory which I traced in homage. And he also goes before us—into the human future, deeper and deeper into God.
Much of what we know about St. Cuthbert is due to the eighth-century writings of the Venerable Bede, the great scholar-monk of the Early Middle Ages. A teenager when Cuthbert died, Bede remains linked to Cuthbert by more than his writing. His own remains, enclosed in a silk bag, were housed with Cuthbert’s at Durham for 348 years, until given their own separate shrine in 1370. After the English Reformation put an end to shrines, Bede’s remains were reburied in the floor of Durham’s Galilee Chapel, at the opposite end of the cathedral from Cuthbert’s tomb. To walk the length of the interior, from Bede in the west to Cuthbert in the east, felt like a recapitulation in miniature of my entire pilgrimage. Every step a prayer.
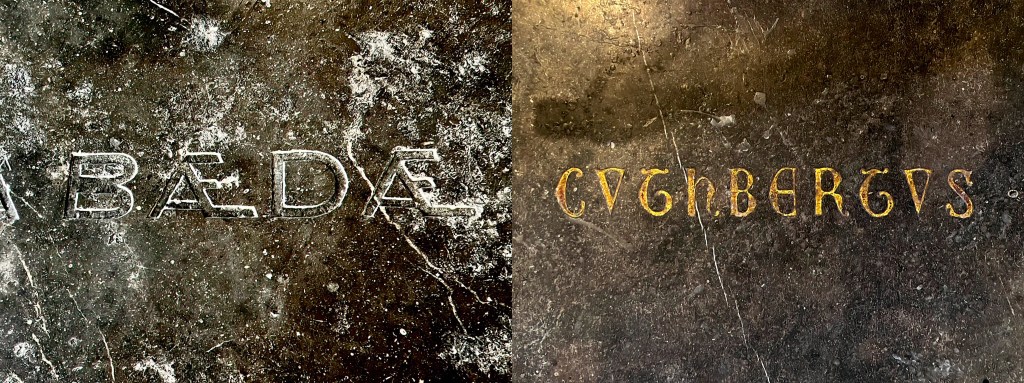
When I made my plans to visit Durham after St. Cuthbert’s Way, I neglected to check my liturgical calendar, so it was a wonderful surprise to learn I had arrived on the very eve of Bede’s feast day and—to my further amazement—in the thousandth year since the Translation of his Relics into Cuthbert’s tomb. What a glorious conclusion to my pilgrimage! It was pure gift, not something I had thought up in advance. That evening I joined a sung eucharist, celebrated at Bede’s final resting place in the Galilee Chapel. His simple stone tomb served as the altar. As incense drifted through the forest of stone columns, the choir sang William Byrd’s exquisite Mass for Four Voices, and the congregation added our own voices in exuberant hymnody.



Recalling Bede’s significance as “the father of English learning,” we prayed for “all biblical scholars and writers and all who translate and interpret your word in every part of the world.” Praising God for Bede the historian, we prayed for “church historians and all who interpret the past to strengthen witness in the present.” And we sang,
For his example we give thanks,
His zeal to learn, his skill to write;
Like him we long to know God’s ways
And in God’s word drink with delight …
Teach us, O Lord, like Bede to pray,
To make the word of God our joy,
Exult in music, song and art,
in worship all your gifts employ. [viii]
The next evening, on the feast itself (May 25), a beautiful Evensong was held in the main church, followed by a procession of clergy, choir and people to the Galilee Chapel. Since I was sitting at the front of the nave, I was the first to leave my pew to trail the choir. For a moment I wondered if I had misunderstood the instructions in the bulletin. No one else seemed to be joining me. Uh-oh, I thought, worrying that this bumbling priest from the Colonies was violating liturgical decorum. Then, to my relief, others began to step into the aisle, and together we made our way to Bede’s tomb, singing a hymn to the glorious tune of Westminster Abbey:
Here in England, through the ages,
While the Christian years went by,
Saints, confessors, martyrs, sages,
Strong to live and strong to die,
Wrote their names upon the pages
Of God’s blessèd company. [ix]
The Galilee Chapel was soon packed with worshippers. I was herded into a spot in front of the tomb, just three feet from the lead boy soprano. Though his body was small and willowy, it produced sounds of astonishing amplitude and soaring clarity in anthems by Palestrina, Tallis, and Edwin George Monk. I’ve never stood so near a voice so beautiful. The nineteenth-century Anglican cleric Sidney Smith said that his idea of heaven was eating pâté de foie gras to the sound of trumpets. For me, heaven would be standing three feet from the angel choir. I could skip the goose liver.
At one point in the liturgy, one of Bede’s most memorable stories was read aloud: the Anglo-Saxon parable of the sparrow in the banqueting hall, to my mind one of the best existential arguments for places like Durham Cathedral to exist—they nourish and perpetuate a way of knowing that is the alternative to despair. Here’s how Michael York tells the story in a video I made in 1988, The Story of Anglicanism.
The morning after Bede’s feast, I took a train to London. As a coda to my Cuthbert pilgrimage, I wanted to see the two books at the British Library with close connections to the saint. One was a pocket-size copy of John’s Gospel, discovered in Cuthbert’s coffin four centuries after his death. It may have been his personal copy, or a posthumous tribute placed near his body by a fellow monk. It is the oldest European book still in its original binding.

Cuthbert loved the Fourth Gospel. When Boisil, his old monastic mentor, told him he expected to die within seven days, Cuthbert asked him, “Which book would it be best to read if we only have a week?” Boisil replied, “The Evangelist John.” And for the next seven days, until Boisil’s death, the two monks did Bible study together. Bede, who recorded this story for posterity, added a comment: “They dealt with only the simple things of the faith which worketh by love and not deep matters of argument.” [x]

The other treasure I had to see was the Lindisfarne Gospels, one of the most beautiful books ever made. Thought to be the work of a single man, Eadfrith, third bishop of Lindisfarne after Cuthbert, it was laboriously produced a few decades after the saint’s death, “for God and St. Cuthbert and all the holy people who are on the island.” It was probably displayed for veneration at the saint’s shrine at Lindisfarne until the ninth-century Viking incursions. When Cuthbert’s remains and relics began the long exodus that ended in Durham, the Lindisfarne Gospels went with them.
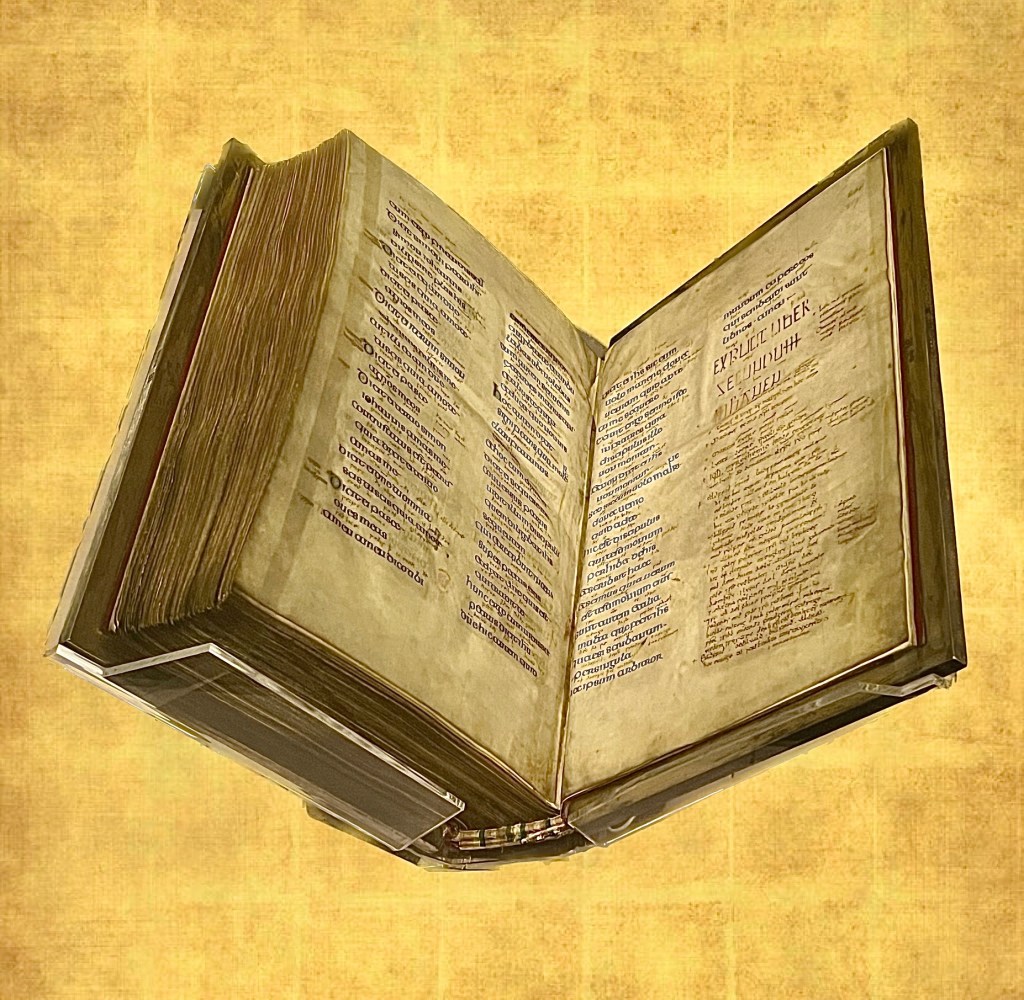

Alas, the two pages on view during my visit contained no images, only text. The Latin was written in the handsome “Insular half-uncial” script. Between the lines is a word-by-word translation into a Northumbrian dialect of Old English, added in the tenth century by a priest named Aldred. Although librarians may shudder at the thought of a book being defaced by a reader, Aldred, I presume, was trying to make the gospels more readable. In any case, his scribbles have the honor of being the earliest surviving translation of the gospels into English.

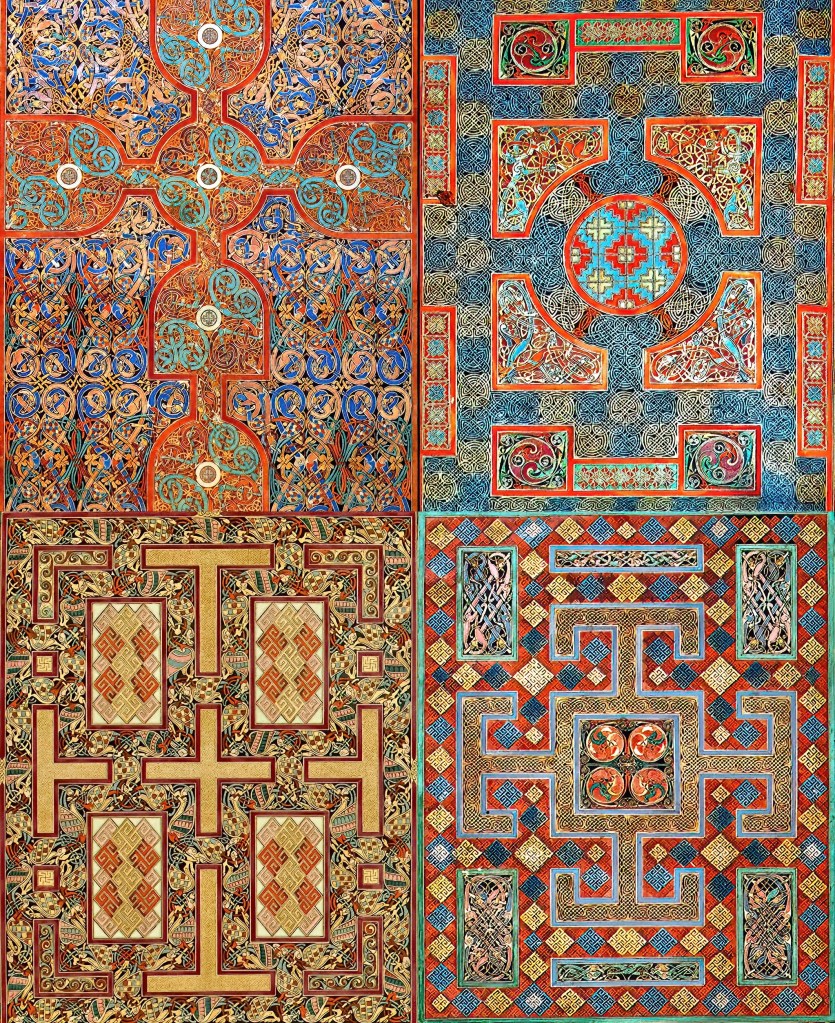
What I had most hoped to see was one of this book’s celebrated illuminations, particularly the “carpet pages,” a suite of four variations on the symbol of the Cross, embedded within mesmerizing patterns, both abstract and zoomorphic. Michelle P. Brown, a longtime curator of the Lindisfarne Gospels, calls these pages “[painted] labyrinths of prayer, prefiguring the devotional pavement-mazes of Chartres and other of the Gothic cathedrals by half a millennium or more.” [xi] Although my eyes had not seen the glory of those magic carpets of colored ink, I departed the British Library in peace. A glimpse of the book itself was enough—for now.

On my last day in Durham, there had been a splendid noonday choral concert in the cathedral by students from southern California’s Pomona College. That school is near a parish where I once served, and the connection delighted me—a taste of home in a faraway land. With St. Cuthbert’s Way behind me and God knows what before me, their final song spoke a word of grace and blessing to my pilgrim heart.
I’ll be on my way, I’ll be on my way;
I’ll have laid my frown and all my burdens down,
I’ll be putting on my crown,
I’ll be on my way.When I am gone, don’t you look for me in the places I have been;
I’ll be alive but somewhere else, I’ll be on my way again! [xii]
With thy wonted loving-kindness hear thy servants as they pray,
And thy fullest benediction shed within its walls alway.
Photographs and videos are by the author.
[i] J. G. Davies, Temples, Churches and Mosques: A Guide to the Appreciation of Religious Architecture (New York: The Pilgrim Press, 1982), 152-153.
[ii] Steen Eiler Rasmussen, quoted in Thomas Barrie, Spiritual Path, Sacred Place: Myth, Ritual, and Meaning in Architecture (Boston, MA: Shambhala Publications, 1996), 46.
[iii] Le Corbusier (1887-1965), designed one of the landmark examples of modern religious architecture, Notre Dame du Haut at Ronchamp, France. Though not a Christian believer, he believed in the power of architecture to create a spiritual environment. Quoted in James Pallister, Sacred Spaces: Contmporary Religious Architecture (New York: Phaidon Press, 2015), 9.
[iv] T. J. Gorringe, A Theology of the Built Environment: Justice, Empowerment, Redemption (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002), 258.
[v] G. K. Chesterton, quoted in Steven J. Schloeder, Architecture in Communion: Implementing the Second Vatican Council through Liturgy and Architecture (San Francisco: Ignatius Press, 1998), 227.
[vi] Michael Camille, quoted in Philip Sheldrake, Spaces for the Sacred: Place, Memory, Identity (Baltimore, MD: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 2001), 58.
[vii] T. S. Eliot, “Little Gidding” (1942) in Four Quartets.
[viii] “We sing to God in praise of Bede,” text by Rosalind Brown.
[ix] “God, whose city’s sure foundation,” text by C. A. Alington.
[x] From Bede’s Life of St. Cuthbert, quoted in Philip Nixon, St. Cuthbert of Durham (Gloucestershire, UK: Amberly Publishing, 2012), 28.
[xi] Michelle P. Brown, The Lindisfarne Gospels: Society, Spirituality & the Scribe (London: The British Library, 2003), 77-78. Brown curated a 2003 exhibition, “Painted Labyrinths: The World of the Lindisfarne Gospels,” so I added “painted” to the citation from her book.
[xii] Shawn Kirchner, “I’ll Be On My Way,” can be heard on his album, Meet Me on the Mountain (2006). The Pomona College Glee Club is under the direction of Donna M. Di Grazia. Their entire program was inspiring and beautifully sung—one of the highlights of my journey.







